About Us
Thermal bridges are highly conductive structural elements that create heat transfer between the exterior and interior of the building thermal envelope. Thermal bridging occurs through any material that is more conductive than the insulation surrounding it. The conductive heat transfer due to thermal bridging has been recognised as a considerable factor in building envelope heat loss.
Thermal bridging through steel and concrete structures can therefore have a significant impact on a building’s energy performance. Thermal bridging can reduce the R value of a wall assembly by as much as 50% by interrupting continuous insulation. Reducing heat flow through a building’s thermal envelope reduces energy consumption as well as potential condensation issues. To achieve higher R values, thermal bridging and air leakage must be minimised.
As early as 2006, many European countries had already instituted improved energy rating systems for new buildings to better control and reduce domestic energy consumption. Nearly 10 years ago, in response to an EU initiative to improve the energy performance of buildings even further, Armadillo Ltd. developed its first thermal break material, Armatherm™ to prevent heat loss due to thermal bridging.
Since 2011, drawing on Armadillo Ltd.’s experience, Armatherm™ has been working with architects and structural engineers in North America to improve building design details and reduce heat loss due to thermal bridging within the building thermal envelope.
Products
-
Balcony Canopy Thermal Bridging Solution For Architects

-
Foundation Wall Thermal Break

-
Masonry Shelf Angle Thermal Bridging Solution For Structural Engineers

-
Balcony Thermal Break Material

-
Cladding Thermal Break For Fabricators

-
Column Base Thermal Bridging Solution For Fabricators

-
Masonry Shelf Angle Thermal Break For Architects

-
Parapet Roof Penetration Thermal Break For Fabricators
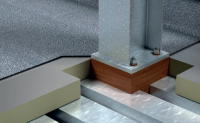
-
Parapet Roof Penetration Thermal Bridging Solution For The Construction Industries
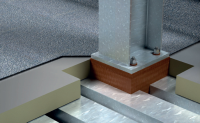
-
Masonry Shelf Angle Thermal Bridging Solution

News
-
How effective are thermal breaks?

-
What’s the difference between a thermal bridge and a thermal break?

-
New Global Certification for Armatherm Structural Thermal Break Material

-
The use of thermal breaks in cold storage facilities

-
The importance of using thermal break materials with the right compressive strength
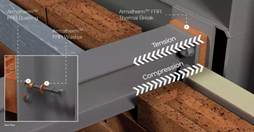
-
Armatherm™ partners with Hanley Wood offering thermal bridging webinar

-
How to make flat roof systems energy efficient

-
Armatherm achieves Passivhaus Column Base certificate

-
One of the leading suppliers of thermal break exhibits at London Build Expo 2022

-
Armatherm’s 2023 Exhibitor Events…


